Consult Best Neurologist in Raipur
Dr. Ritesh Sahu is one of the "best neurologist in Raipur. Consult neuro physician in Raipur for neurological diseases like headache, migraine, neuropathy, Parkinson's, multiple sclerosis, and many more conditions.
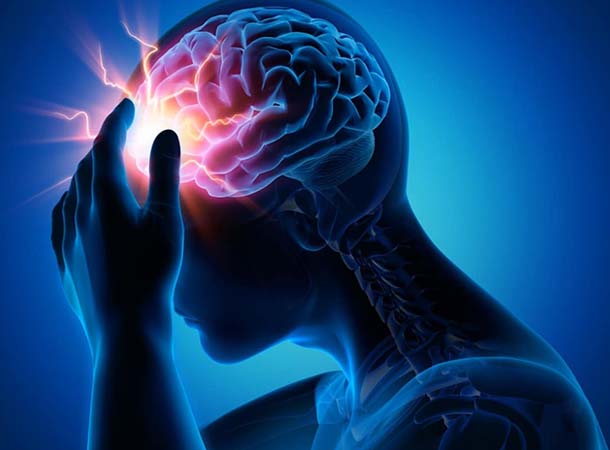
Diseases of brain
Brain diseases come in different forms. Infections, trauma, stroke, seizures, and tumors are some of the major categories of brain diseases. Here's an overview of various diseases of the brain.
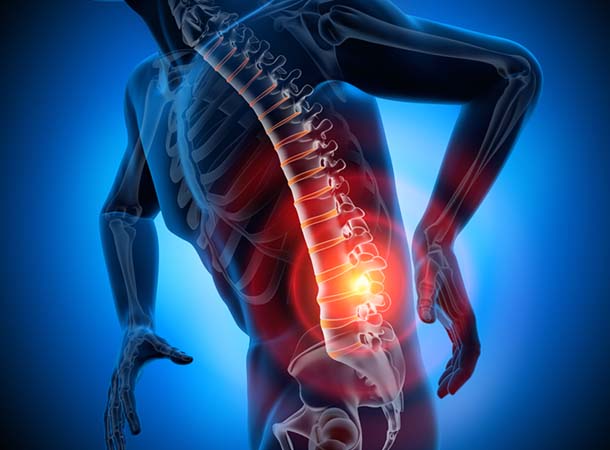
Read More +Spinal Cord
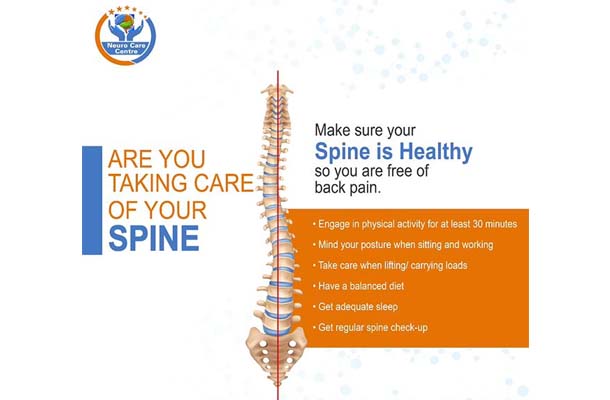
Your spinal cord is a cylindrical structure that runs through the center of your spine, from your brainstem to your low back. It's a delicate structure that contains nerve bundles and cells that carry messages...
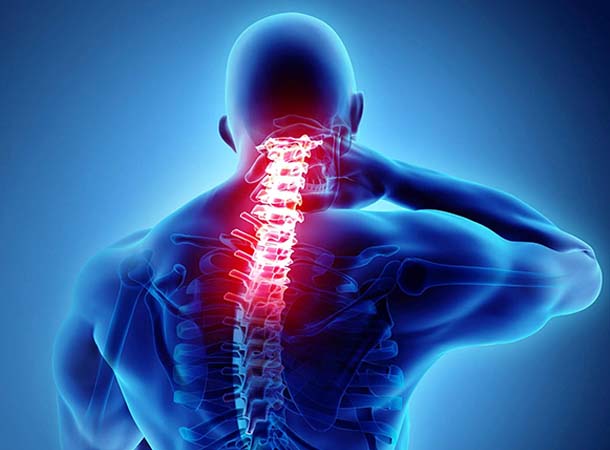
Read More +Neuromuscular disorder
Nerves are like cables that carry electrical impulses between your brain and the rest of your body. These impulses help you feel sensations and move your muscles. They also maintain certain autonomic functions...
Read More +Electroencephalography (EEG)
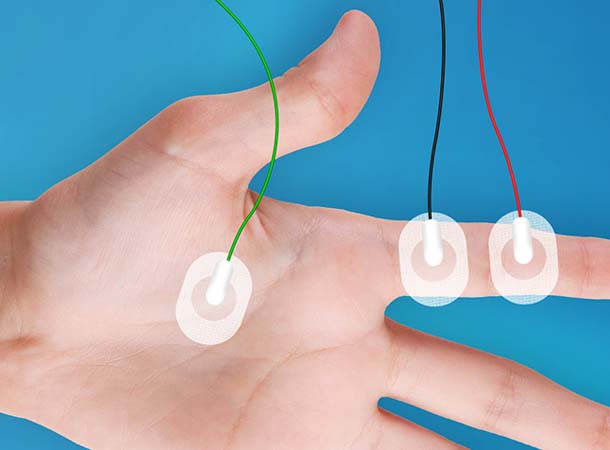
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a test that measures electrical activity in the brain using small, metal discs (electrodes) attached to the scalp.
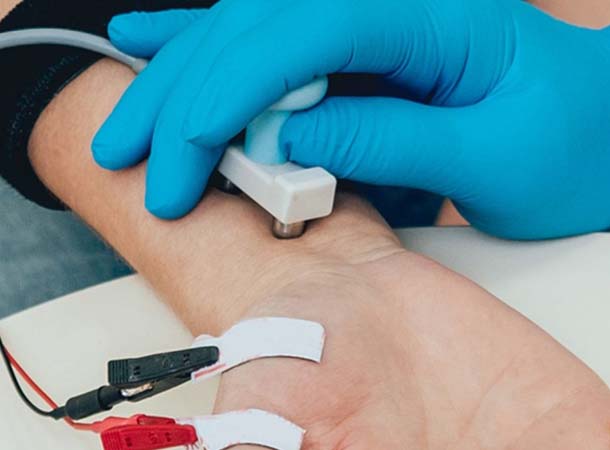
Read More +Nerve conduction velocity study (NCV)
A nerve conduction velocity (NCV) test — also called a nerve conduction study (NCS) — measures how fast an electrical impulse moves through your nerve. NCV can identify nerve damage.
Read More +Electromyography (EMG)
Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic procedure to assess the health of muscles and the nerve cells that control them (motor neurons). EMG results can reveal nerve dysfunction, muscle dysfunction or....
Read More +